
We have collated all possible questions that could be asked in the interviews. These questions will help you to understand the concepts in more details as well as those will prepare for the interview. There are more than 300 questions that have been collected either from interviews asked in MNCs or defined to understand the concepts.
What is PV or pharmacovigilance?
Pharmacovigilance (PV or PhV), also known as Drug Safety, is the pharmacological science relating to the collection, detection, assessment, monitoring, and prevention of adverse effects with pharmaceutical products.
Why pharmacovigilance is important? Or What are the Objectives of PV?
Following are the objectives that make PV important:
Early detection of unknown or insufficiently documented adverse effects and interactions.
Detection of an increase of the frequency of a known adverse effect.
Identification of risk factors and mechanisms that are at the basis of the occurrence of adverse effects.
Continuous reevaluation of the risk-benefit balance of medicines.
Distribution of information about adverse effects and interactions so that they occur less frequently and in order to have less therapeutic errors.
What are the different phases of Clinical Trials?
Phase | Primary Aim | Dose | Number of patients | Notes |
I | Testing of drug on healthy volunteers for dose-ranging | Often sub therapeutic, but with ascending doses | 20-100 | Determines whether drug is safe to check for efficacy |
II | Testing of drug on patients to assess efficacy and safety | Therapeutic dose | 100-300 | Determines whether drug can have any efficacy; at this point, the drug is not presumed to have any therapeutic effect whatsoever |
III | Testing of drug on patients to assess efficacy and safety | Therapeutic dose | 1000-2000 | Determines a drug’s therapeutic effect; at this point, the drug is presumed to have some effect |
IV | Post marketing surveillance | Therapeutic dose | anyone seeking treatment from their physician | Watch drug’s long term effects |
What is clinical research?
Clinical research is a branch of medical science that determines the safety and effectiveness of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens intended for human use. These may be used for prevention, treatment, diagnosis or for relieving symptoms of a disease.
What is Pre-clinical Phase, Phase 0 and Phase V?
Phase | Primary Aim | Dose | Number of patients | Notes |
Pre- Clinical | Testing of drug in non-human subjects, to gather efficacy, toxicity and pharmacokinetic information | Unrestricted | Not applicable (in vitro and in vivo only) | |
Phase 0 | Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics particularly oral bioavailability and half-life of the drug | very small, sub-therapeutic | 10 people | Often skipped for phase I |
Phase V | Translational research | No dosing | All reported use | Research on data collected |
What is valid case?
The case which satisfies following four criteria will be considered as valid case
- Identifiable reporter
- Identifiable patient
- Suspect drugs
- Adverse event.
What is AE / Adverse event?
Any untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical investigation subject administered a pharmaceutical product and which does not necessarily have a causal relationship with this treatment.
What is ADR / adverse drug reaction?
All noxious and unintended responses to a medicinal product related to any dose should be considered adverse drug reactions.
What is the difference between AE and ADR?
The main difference between AE and ADR is about the causality of the event with suspect drug. AE may or may not have causal relationship with the event but ADR must have causal relationship with an event.
What is SUSAR?
SUSAR is Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse reaction. Serious adverse drug reaction (SAR) that is unexpected (per the product labels such as USPI, SPC etc.) or for which the development is uncommon (unexpected issue) observed during a clinical trial and for which there is a relationship with the experimental drug, whatever the tested drug or its comparator.
What is SAE?
Serious Adverse Event (SAE) or Serious Adverse Drug Reaction (Serious ADR) is any untoward medical occurrence that at any dose which
- results in death,
- is life-threatening,
- requires inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization,
- results in persistent or significant disability/incapacity, or
- is a congenital anomaly/birth defect.
What is PSUR?
PSUR is Periodic Safety Update Report. Periodic safety update reports (PSURs) are pharmacovigilance documents intended to provide an evaluation of the risk-benefit balance of a medicinal product for submission by marketing authorization holders at defined time points during the post-authorization phase.
Which form is used for voluntary reporting in USA?
MedWatch form 3500 is used for voluntary reporting in US FDA.
Which form is used for mandatory reporting in US FDA?
MedWatch form 3500A is used for mandatory reporting in US FDA
What are the timelines for ICSR submissions?
As per GVP guidelines, following are the timelines for submission of ICSRs:
Sr. No. | Case | Time line |
1. | Fatal or Life-Threatening Unexpected ADRs (SUSARs) |
|
2 | All Other Serious, Unexpected ADRs |
|
3 | All Non serious cases |
|
What is the difference between concomitant medication and past drugs?
The concomitant medications are the drugs which were started prior to suspect drug or taken at the same time and continued to take when suspect drug was administered. If these drugs are stopped within the 30 days prior to event onset should be considered as concomitant medications. But, Whereas, the past drugs are defined as the drugs taken prior to start of suspect drugs.
What is the difference between concurrent medical conditions and medical history?
The diseases or conditions prior to start of suspect drugs are considered as medical history.
The diseases present at the time when patient is taking suspect drugs are called as concurrent conditions or illness.
How do you capture information for concomitant medication?
The brand name of the drug, start date, stop date and indication will be captured for concomitant medications.
What are the sources for ICSR reporting?
Following are the sources ADR/ICSR reports:
Unsolicited Reports:
- Spontaneous reports
- Literature reports
- Reports from other sources
- Information on suspected adverse reactions from the internet or digital media
Solicited Reports:
- Clinical Trial (CT)
- Non-interventional study/program (NIS/NIP)
- Post approval patient use programs
- Patient support and disease management programs
- Compassionate use
- Patient compliance programs
What is HCP?
HCP is the Heath care professional.
Who should be considered as HCP?
The physician, pharmacist, registered nurse etc. should be considered as HCP.
What is MedDRA?
MedDRA is the Medical dictionary for regulatory activities. It is developed by ICH.
What is WHODD?
WHODD is the World Health Organization Drug Dictionary. It is developed by WHO.
Where the global ICSRs are collected by WHO?
The global ICSRs are collected by WHO at Upsala Monitoring Center (UMC), Sweden.
What is litigation?
Litigation means laws and regulations. In concern with PV, litigation means the laws related to drugs.
What is labeling? What are the labeling documents?
In PV, labeling is the procedure to find the expectedness of event in safety reference documents. Expectedness means the sponsor has agreed that certain adverse events were caused due to their drug and those events were documented in safety referenced documents. There are four major safety reference documents and these are IB, CDS, EUSPC and USPI.
What is the difference between severity and seriousness?
Severity defines the intensity of an adverse event which will be mild, moderate and severe whereas seriousness defines the 5 seriousness criteria of SAE.
What is blinding?
A procedure in which one or more parties to the trial are kept unaware of the treatment assignment. Single-blinding usually refers to the subject being unaware, and double-blinding usually refers to the subject, investigator, monitor, and, in some cases, data analyst(s) being unaware of the treatment assignment. However, in triple blind studies, subject, investigator and the bio-statistician are kept unaware of the treatment assigned to patients. This helps to avoid the treatment bias.
What are the source documents?
The informed consent form, medical prescriptions, lab test results (x-ray, CT scan report, hematology tests etc) and investigators notes, are the source documents.
What is CIOMS?
Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences
Which Form is widely used for ADR reporting?
CIOMS form I is widely used for ADR reporting.
What is comparator?
An investigational or marketed product (i.e., active control), or placebo, used as a reference in a clinical trial.
What is randomization?
The process of assigning trial subjects to treatment or control groups using an element of chance to determine the assignments in order to reduce bias.
What is the process flow in pharmacovigilance?
The process flow in pharmacovigilance is as follows
- AE reports
- Aggregate Reporting
- Signal Detection
- Risk Management
Which is the drug regulatory authority of India?
Central Drug Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is the drug regulatory body/authority of India.
What is the timeline for the death or life-threatening SUSAR cases?
As per the regulatory authority all death and life-threatening SUSAR cases should be reported within 7 calendar days to regulatory authority by sponsor.
Check the validity for the following cases.
{Hint note: case is valid only when it satisfy the four validity criteria’s ie patient, reporter, suspect drug and event}
The patient reported that she is suffering from chest pain since Apr 2013. She was prescribed atenolol by physician.
The case is invalid. The information provided was Reporter and Patient: Female patient, Event: Chest pain but lacks suspect drug.
The physician reports that a male patient experienced a pneumonia after ingestion of Drug A. He was treated with antibiotics.
The case is valid. The information provided was – Reporter: Physician, Patient: Male, Event: Pneumonia and Suspect Drug: Drug A. Hence it satisfies the four validity criteria.
Narrative Writing Questions:
Write narrative for the following information
Report | Spontaneous |
Reporter | Patient |
Patient details | 21 Year old female |
Suspect drug | Drug A (start date: 25 Apr 2013, Dose: 30 mg twice a day) |
Event | Pneumonia (30 Oct 2013) |
Treatment drugs | Ciprofloxacin and Azithromycin (25 mg once day) |
Other conditions | Back pain (2010 to 2011), hypertension (2010 and ongoing), Head injury (2010), |
Other drugs | Amlodipine (11 Jan 2013 to 21 Apr 2013), Aspirin (12 Apr 2013 and ongoing) |
Lab tests | X-ray (30 Oct 2013) showed pneumonia Hematology test (31 Oct 2013) results pending |
Ans: The following will be sample narrative.
This is a spontaneous report received from 21 year old female patient who experienced pneumonia while taking Drug A.
Her medical history includes back pain and head injury. Her concurrent conditions included hypertension. Her concomitant drug includes aspirin. Her past drugs included amlodipine.
On 25/Apr/2013, she started therapy with drug A (30 mg twice a day) for unknown indication. On 30/Oct/2013, she experienced pneumonia. Subsequently, her x-ray showed pneumonia and started treatment with ciprofloxacin and azithromycin (25 mg once day). On 31/Oct/2013, her hematology test was preformed (results were pending).
At the time of this report, the outcome of pneumonia and ongoing status drug A was not reported.
The reporter did not provide seriousness and causality for pneumonia with suspect drugs.
No further information was provided.
[Note: back pain and head injury occurred prior to start of suspect drug A, hence considered as medical history. Hypertension is ongoing at the time of suspect drug administration hence taken as concurrent condition. Similarly, aspirin was ongoing at the time of suspect drug administration, hence considered as concomitant medication. Amlodipine was stopped prior to start of suspect drug A, hence should be considered as past drug].
Write narrative for the following case information:
Report | Clinical Trial protocol ABC: Open label, comparative study of drug A and B in NSCLC patients. |
Reporter | Investigator – Dr. Anderson |
Patient details | 68 Year old male patient with NSCLC Subject number: 0123 |
Suspect drug | Drug A (start date: 25-Apr-2014, Dose: 30 mg twice a day) |
Event | Anaphylactic shock (30 Oct 2013) (Grade 2) |
Treatment drugs | No treatment was given but study drug was stopped in response with the event. |
Other conditions | hypertension (2000), Head injury (2011), |
Other drugs | Atenolol (11 Jan 2013 to 21 Apr 2013), Aspirin (12 Apr 2013 and ongoing) |
Lab tests | No Labs performed |
ANSWER: This is a clinical trial report received from Investigator and concerns a 68 year old male subject (subject number: 0123) who experienced anaphylactic shock while enrolled in protocol ABC: Open label, comparative study of drug A and B in NSCLC patients.
His medical history includes head injury. His concurrent conditions included hypertension.
The subject’s concomitant medications included atenolol and aspirin.
On 25-Apr-2014, the subject started therapy with drug A at dose of 30 mg twice a day (route and form: no reported) for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
On 30-Oct-2014, the subject experienced grade 2 anaphylactic shock reaction (symptoms not reported) for which patient received no treatment but study drug A was stopped.
No laboratory tests were performed.
At the time of this report, the outcome of anaphylactic shock was not reported.
In response to the event, study drug A was discontinued on an unspecified date.
The reporter did not provide the seriousness and causality assessment for the event anaphylactic shock with study drug A.
What is VAERS?
The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System.
What is Eudravigilance?
EudraVigilance (European Union Drug Regulating Authorities Pharmacovigilance) is a data processing network and management system for reporting and evaluating suspected ADRs during the development and following the marketing authorization of medicinal products in the European Economic Area (EEA).
What is GVP?
GVP stands for Good Pharmacovigilance Practice guidelines for EU.
Please explain the MedDRA levels?
There are five levels in MedDRA. There are as follows:
- System Organ Cloass (SOC): Highest level of the terminology, andrepresenting an anatomical or physiological system,etiology, or purpose.
- High Level Group Term (HLGT): Subordinate to SOC, superordinate groupingfor one or more HLTs.
- High Level Term (HLT): Subordinate to HLGT, superordinate groupingfor one or more PTs.
- Preferred Term (PT): Represents a single medical concept
- Low Level Term (LLT): Lowest level of the terminology, related to a single PT as a synonym, lexical variant, or quasis-synonym m (Note All PTs ha e an identical LLT)
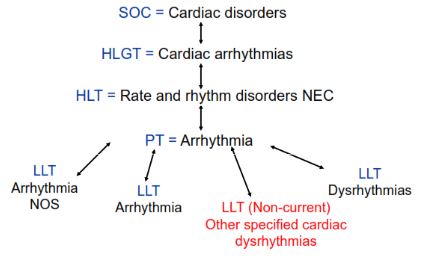
Fig.: MeDDRA Levels
Enlist the modules of GVP?
# See in Tutorial section for: Pharmacovigilance regulations
Enlist the PV guidelines from ICH?
# See in Tutorial section for: Pharmacovigilance regulations
What is FAERS?
The FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) is a database that contains information on adverse event and medication error reports submitted to FDA.
What is VigiBase?
The VigiBase data resource is the largest and most comprehensive in the world, and it is developed and maintained by the UMC on behalf of the World Health Organization.
What is Risk management system?
A set of pharmacovigilance activities and interventions designed to identify, characterize, prevent or minimize risks relating to medicinal products including the assessment of the effectiveness of those activities and interventions.
What is RMP?
A detailed description of the risk management system.
What is signal detection?
Reported information on a possible causal relationship between an adverse event and a drug, the relationship being previously unknown or incompletely documented is called as signal. The process for detection of signal is called as signal detection.
What are different methods for signal detection?
Following methodologies were used:
Review of individual case safety reports
Statistical analyses of large database
Combination of both ICSR review and statistical analyses
What are the different types of adverse events?
Following types of adverse events:
- Type A: Augmented Pharmacological Effects
- Type B: Bizarre Effects
- Type C: Chronic Effects
- Type D: Delayed Effects
- Type E: End of Treatment Effects
- Type F: Failure of therapy
- Type G: Genetic reactions
- Type I: Idiosyncratic
In brief explain drug discovery process?
Answered yet to add.
What is risk-benefit ratio?
The risk a treatment placed on individual participants versus the potential benefits of the treatment. The risk/benefit ratio may differ depending on the condition being treated.
What is benefit-risk analysis?
Examination of the favorable (beneficial) and unfavorable results undertaking a specific action.
Why risk-benefit balance evaluation of medicines is required?
On the basis risk-benefit balance evaluation the decision will be taken to prevent certain adverse events or discontinuation of drug from the market.
Which volume of EU covers the regulations and guidance for PV in EU?
Volume 9 provides the guidelines and regulations related to PV.
What is Volume 9A?
Pharmacovigilance for medicinal products for Human use
What is the regulatory authority for India, China, USA, Australia?
Answer yet to add.
In which countries a yellow card scheme is used to report ADRs?
United Kingdom (UK)
Enlist the drugs which were withdrawn from the market?
Eg.cerivastatin (brand names Baycol and Lipobay), troglitazone (Rezulin) and rofecoxib (Vioxx)
Is overdose should be reported as adverse event?
Yes. Overdose should be reported as an adverse event.
What is DSUR?
DSUR is the Development Safety Update Report.
Which category of adverse event does the following events fall:
A patient slips on an icy road and suffers severe bruising to her knee. The investigator says this is not related to the IMP and no treatment was required.
Adverse event only.
A patient developed severe headache after taking drug X, The reporting physician considers the event is related to the drug.
Adverse drug reaction
A patient in clinical trial experienced an acute respiratory failure after taking an investigational drug Y. The patient was hospitalized. The investigator considers the event was related with study medication. As per the labeling document (IB), the event was unlisted or unexpected.
SUSAR (suspected unexpected serious adverse reaction)
Read the following scenarios and determine the seriousness criteria does the following events had.
A nurse informed that a 51 year old male diabetic patient was operated for diabetic foot and put on metronidazole infusion drip for 5 days during post-operative period. On day of discharge, the patient had severe gastritis with hematemesis. The patient was administered pantoprazole injection for two days and discharged later.
Hospitalization is the seriousness criteria for the event gastritis with hematemesis.
In which year, the first operating version of Eudravigilance was launched?
In Dec 2001, the first operating version of Eudravigilance was launched.
Which were the agency were merged to form the MHRA?
Medicines Control Agency (MCA) and the Medical Devices Agent (MDA) were merged on 01st Apr 2003, to form the MHRA.
How many zonal centers are in Indian NPVP ?
There are 2 zonal centers in Indian NPVP.
Which E2 guideline provides the guidance for marketed drugs PSURs?
E2C(R1) guideline of ICH provides the guidance for PSURS for marked drugs.
Which 2 parts the EU Risk management plan (EU-RMP) contains?
An evaluation of the need for risk minimization activities and A risk minimization plan are the parts of EU RMP.
What are two different modules EudraVigilance database contain?
EudraVigilance had EVCTM (i.e. Eudravigilance Clinical Trial Module) and EVPM (i.e. Eudravigilance Post-authorization Module) as two different modules.
Enlist the parties involved in ICH?
The six parties were involved in ICH. These are as
1. EU (European Union)
2. EFIPA (European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations)
3. MHLW (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan)
4. JPMA (Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association)
5. FDA (US Food and Drug Administration)
6. PhRMA (Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America).
In which four types the ICH guidelines are divided?
- Quality (Q)
- Efficacy (E)
- Safety (S)
- Multidisciplinary (M)
For which countries or territories, the ICH develops guidelines?
The ICH develops guidelines for US, European Union (EU) and Japan region.
ICH guideline E2D concerns with which standards?
ICH E2D guidelines concerns with Post-marketing expedited reporting standards.
Which ICH guideline describes the data elements that should be used for safety reporting?
ICH E2B(R3) guideline describes the data elements that should be used for safety reporting.
Which CIOMS guidelines provide the pragmatic approaches for current challenges in PV?
CIOMS V guideline provides the pragmatic approaches for the current challenges in PV.
What is 21 CFR part 11?
21 CFR part 11 stands for the Code of Federal Regulations deals with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines on electronic records and electronic signatures in the United States. Part 11, as it is commonly called, defines the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered to be trustworthy, reliable and equivalent to paper records.
What is the timeline for PADER reporting in USA?
The PADER reporting in USA should be quarterly for first three years and annual reports thereafter.
What is the timeline for PSUR reporting in EU?
The PSUR reporting in EU should be every 6 months for two years followed by annually for 3 following years and then 5 years thereafter.
What is SBR or Summary bridging report?
A summary bridging report is a concise document integrating the information presented in two or more PSURs to cover a specified period over which a single report is requested or required by regulatory authorities.
What is REMS?
REMS is the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy.
What are the differences between FDA and MHRA PV inspections?
Difference between US/MHRA PV inspections:
FDA | MHRA | |
Advance Notice | None to a couple of days (US) A few weeks (outside US) | 4 months |
Preparation Phase | Communication of Studies/Products to be reviewed No clear agenda/plan communicated in advance (compliance program guidance manuals publicly available) | Use of pre-inspection questionnaire (SPS) Detailed agenda/plan for the inspection a few days in advance. The company has to identify the most relevant people to discuss each topic listed. |
Conduct Phase | All operational processes covered Inspection style historically data-centered but tends to focus more on processes More data/document review than interviews but changing Duration: 1-3 days 1-2 Inspectors Presentation of early results at closing meeting | All operational processes covered + supporting processes Very process-oriented Very much interview driven Duration: 5 days 3-4 Inspectors Presentation of early results at closing meeting |
Reporting | Very slow if at all Warning letters and FDA 483 immediately. List of deviations without significance rating or proposed corrective actions | Very slow List of deviations with significance rating but no proposed corrective actions |
What are black triangle medicines?
A black triangle on medicine indicates that the medication is under extensive surveillance as either it’s new to the market or that an existing medicine is being used for a new reason or by a new route of administration.
In which region the black triangle is used on medicines.
A black triangle is primarily used in United Kingdom and European Union.
What is orange book of FDA?
FDA publishes the list of approved molecules/drugs for human use yearly in book. This book is known as Orange book.
What is CTCAE?
CTCAE is a grading criterion for the adverse event. CTCAE stands for Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Event. The intensity for any adverse event vary from 1 to 5 (5 is the fatal outcome intensity of the event).
What is the timelines for submitting DSUR to regulatory authorities after the DSUR data lock point.
No later than 60 calendar days.
Which method is used by UMC (Upsala Monitoring Center) for signal detection?
Bayesian combination propagation neural network method is used for signal detection by UMC.
In which year manual reporting was replaced by automation?
In 2002, the manual reporting was replaced by automation.
Which signal detection method is used by FDA and MHRA?
Modified Gamma Poisson Shrinker method used for signal detection by MHRA and FDA.
What is the sequence of phases of inspection process for pharmacovigilance?
Sequence of phases of inspection process for PV are as – Planning, conduct of inspection, reporting and follow up.
What is current electronic ICSR characters limit?
20000 (Twenty thousand) characters is current electronic ICSR character limit.
TMS stands for?
TMS stands for Thesaurus Management System.
For what ATC stands in WHODD?
ATC in WHODD stands for Anatomic Therapeutic Chemical.
What will be the data elements that should be used for duplicate search in clinical cases?
Protocol number, patient number, site number, investigator details and patient’s date of birth can be used for the duplicate search in clinical trial cases.
What is a module VI of GVP guideline?
The module VI of GVP guidelines is Management and Reporting of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products.
Which CIOMS guideline concerns practical issues in pharmacovigilance?
CIOMS V guideline concerns with the practical issues in PV.
As per the WHO scale, what are different causality criteria for event-drug relationship assessment?
As per the WHO scale, following are the various criteria’s for event-drug causality relationship:
- Certain
- Probable/likely
- Possible
- Unlikely
- Conditional/ unclassified
- Unassessible / Unclassifiable
Would you enlist some causality algorithms?
Kramer and ‘Naranjo and jones’ are the causality algorithms.
What is type III allergic ADR?
Type III allergic ADRs ware immune complex mediated, e.g. Serum sickness from anit-thymocyte globulin.
What is the time range for the onset of an acute adverse drug reaction?
The acute adverse drug reaction occurs within 1 hour. Sub-acute ADRs occurs between 1 and 24 hours and latent ADRs will have more than 2 days.
What are the different types of WHO drug dictionaries?
There are following three types of WHO drug dictionaries
WHODD: World Health Organization Drug Dictionary
WHOHD: World Health Organization Herbal Dictionary
WHODDE: World Health Organization Drug Dictionary Enhanced
WHOART: World Health Organization Adverse Reaction Terminology
Which types of adverse events will be detected by signals?
The signals detect the following types of adverse events:
Type B adverse effects
Unusual type A adverse effects
Type C adverse effects
Which signal detection method did UMC use?
The UMC (Upsala Monitoring Center) use “Bayesian Combination Propagation Neutral Network method” to detect signals.
Which signal detection method did FDA and MHRA use?
The FDA and MHRA use ‘Modified Gamma PoissionShrinker Method’ to detect signals form ICSRs.
Enlist three steps for signal detection?
The three steps for signal detection were
Signal detection
Signal Strengthening
Signal follow up
In which year MHRA started yellow card scheme for adverse event reporting?
In 1964, MHRA started yellow card scheme for adverse event reporting.
Enlist the agencies which merged to form MHRA?
On 01-April-2003, the Medicines Control Agency (MCA) and the Medical Devices Agency (MDA) merged to form MHRA.
What is the timeline for submission of REMS submission?
The REMS should be submitted annually for the first 3 years followed by overall at 7 years.
In which year ‘Good Pharmacovigilance Practice (GVP)’ applied in EU?
In July 2002, EMEA adopted/applied good pharmacovigilance practice across the EMEA states.
What is ‘Anzenteikihoukoku’?
The ‘Anzenteikihoukoku’ is the name for PSUR document in Japan.
Which clinical ICSRs in PV database were not reportable?
Following cases from clinical ICSRs in PV database were not reportable:
Clinical unrelated cases (though unexpected)
Non serious cases
What is the notification period for PV inspection from regulatory authority?
There is about 1-3 months of notification period for PV inspection was given by regulatory authority to sponsor/ pharmaceutical company.
What are different phases of inspections?
There are following phases of PV inspection:
Planning
Conduction of inspection
Reporting and follow up.
What is CAPA stands for?
CAPA stands for Corrective Action Preventive Action.
What are the different meetings held by inspector with sponsor/ pharmaceutical company?
There are generally following three types of meetings were held by inspector with pharmaceutical company:
Opening meeting
Interim meeting
Closing meeting
What are the essential documents in clinical trials?
Following were the essential documents in clinical trials:
Investigator Brochure
Protocol
Informed consent form
Regulatory approvals
Financial aspects/insurance
CIOMS established in which year?
In 1949, CIOMS (The Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences) was established jointly by WHO and UNESCO.
Enlist various pre-marketing reports submitted by sponsor to regulatory authority?
Various pre-marketing reports submitted by sponsor to regulatory authority were as follows:
NDA & ANDA Annual Reports
IND annual reports
Clinical Study Reports (CSR)
What was the reason to withdraw VIOXX drug form market?
The drug VIOXX was withdrawn form market due to increased cardiovascular event risks such as heart attacks and strokes.
EU-RMP plan consist of how many parts?
EU-RMP plan consist of two parts:
Part I: a. Safety Specification, b. Pharmacovigilance plan.
Part II: a. Risk management, b. An evaluation of the need for risk minimization.
When does the event of overdose should be captured in database?
Event of overdose should be captured only when it’s specifically reported as overdose else it will be captured as medication error.
If you have received follow up to fatal SUSAR case. What will be the processing timeline for this case?
As per the regulations, only initial SUSAR cases will have the reporting time frame of 7 day, after follow up we can submit the ICSR after normal 15 days.
Write the long form for followings:
ADR: Adverse Drug Reaction AE: Adverse Event ANDA: Abbreviated New Drug Application ASR: Annual Safety Report BLA: Biologics License Application CBER: Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research CDER: Center for Drug Evaluation and Research CDS: Company core Data Sheet CDSCO: Central Drugs Standard Control Organization CHMP: Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use CIOMS: Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences CMDh: Coordination group for Mutual recognition and Decentralized procedures – Human COSTART: Coding System for a Thesaurus of Adverse Reaction Terms CPD: Company Product Dictionary CRF: Case Record form CRO: Contract Research Organization CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Event. DCGI: Drug Controller General (India) DSUR: Drug Safety Update Report EEA: European Economic Area EMA: European Medicines Agency eCRF: Electronic Case Record Form EUSPC: European Union Summary of Product Characteristic GCP: Good Clinical Practice GMP: Good Manufacturing Practice GVP: Good Pharmacovigilance Practice HCP: Health Care Professional IB: Investigator’s Brochure | ICSR: Individual Case Safety Report ICH: International Conference on Harmonization IEC: Independent Ethics Committee IND: Investigational New Drug application IRB: Independent Review Board ISS: Investigator Sponsored Studies MedDRA: Medical Dictionary Regulatory Activities NCI: National Cancer Institute NDA: New Drug Application NIP: Non interventional Program NIS: Non Interventional Study PADER: Periodic Adverse Drug Experience Reports PBRER: Periodic benefit- risk evaluation report PRAC: Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee PSMF: Pharmacovigilance System Master File PSUR: Periodic Safety Update Report PV: Pharmacovigilance RMP: Risk Management Plan SAE: Serious Adverse Event SBR: Summary Bridging Report SOC: System Organ Class SOP: Standard Operating Procedure SUSAR: Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse Reaction UMC: Upsala Monitoring Center USFDA: United States Food Drug Administration USPI: United States Package Insert VAERS: Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System WHOART: WHO Adverse Reaction Technology WHO: World Health Organization QPPV – Qualified Person for Pharmacovigilance. WHODD: World Health Organization Drug Dictionary |
Match the pairs for guidelines:
Guideline Code | Guideline Name | Ans |
|
| a-5 |
|
| b-13 |
|
| c-9 |
|
| d-10 |
|
| e-7 |
|
| f-15 |
|
| g-18 |
|
| h-1 |
|
| i-2 |
|
| j-16 |
|
| k-12 |
|
| l-20 |
|
| m-17 |
|
| n-6 |
|
| o-4 |
|
| p-3 |
|
| q-14 |
|
| r-8 |
|
| s-11 |
|
| t-19 |
Match the pairs for drug withdrawn from market for adverse events:
Drug | Events | Ans |
|
| 1-c |
|
| 2-h |
|
| 3-j |
|
| 4-a |
|
| 5-i |
|
| 6-b |
|
| 7-b |
|
| 8-e |
|
| 9-g |
|
| 10-d |
Match the pairs for Regulatory authority:
Country | Regulatory Authority | Ans |
|
| a-8 |
|
| b-5 |
|
| c-9 |
|
| d-6 |
|
| e-1 |
|
| f-4 |
|
| g-2 |
|
| h-10 |
|
| i-7 |
|
| j-3 |
Hope these questions will help you to crack the interview and get the job. If you come across any new questions that you want to share with me, please do add those questions in comment section and I will try to help you with all possible ways. Hence, your comments are more important to me. Thank you and Best of luck!! 🙂
This truly is a great website, thank you so much for putting up all this knowledge I’ve never seen any advanced PV ressources online !
LikeLiked by 1 person
I read your blog, it was very useful for me. I request you to keep continue to post related to Drug Discovery CRO
LikeLike